The lab works on robust, identifiable and interpretable machine learning tools for scientific inference. We work on both core machine learning topics and the application of machine learning algorithms for scientific inference in the life sciences. Our research focus is on:
- Representation learning, especially using contrastive learning and generative pre-training
- Hierarchical representation learning
- Identifiability and robustness of machine learning algorithms
- (Nonlinear) dynamical system modeling
The following is a list of selected pre-prints and publications published by lab members (including work done at previous institutions). For a full list, please see Google Scholar.
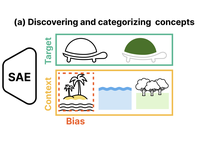
ConceptScope: Characterizing Dataset Bias via Disentangled Visual Concepts
ConceptScope is a scalable and automated framework for analyzing visual datasets by discovering and quantifying human-interpretable …
Equivariance by Contrast: Identifiable Equivariant Embeddings from Unlabeled Finite Group Actions
EbC learns equivariant embeddings from observation pairs without relying on group-specific inductive biases, with theoretical …
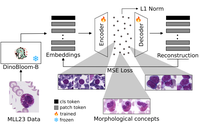
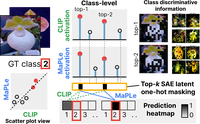
CytoSAE: Interpretable Cell Embeddings for Hematology
CytoSAE is a sparse autoencoder for interpretable cell embeddings in hematology, enabling discovery of morphologically relevant …
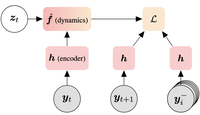
xCEBRA: Time-series Attribution Maps with Regularized Contrastive Learning
xCEBRA generates attribution maps with identifiability guarantees for time-series data using regularized contrastive learning and a new …
Sparse Autoencoders Reveal Selective Remapping of Visual Concepts During Adaptation
PatchSAE is a framework to extract interpretable concepts and their spatial attributions in vision transformers.
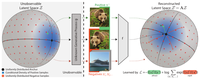
Self-supervised contrastive learning performs non-linear system identification
DCL is a framework for non-linear system identification using contrastive learning.
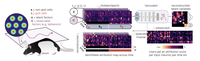
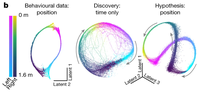
Learnable Latent Embeddings for Joint Behavioral and Neural Analysis
CEBRA is a contrastive learning algorithm for relating behavior and neural activity.
Contrastive Learning Inverts the Data Generating Process
Contrastive learning with the InfoNCE objective can recover the ground truth latent factors underlying the data.
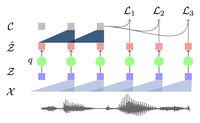
vq-wav2vec: Self-Supervised Learning of Discrete Speech Representations
Learning discrete representations of speech yields state-of-the-art recognition performance on TIMIT and WSJ.
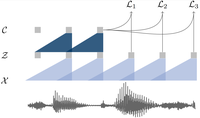
wav2vec: Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition
Contrastive pre-training on speech at scale reduces the need for labeled data.